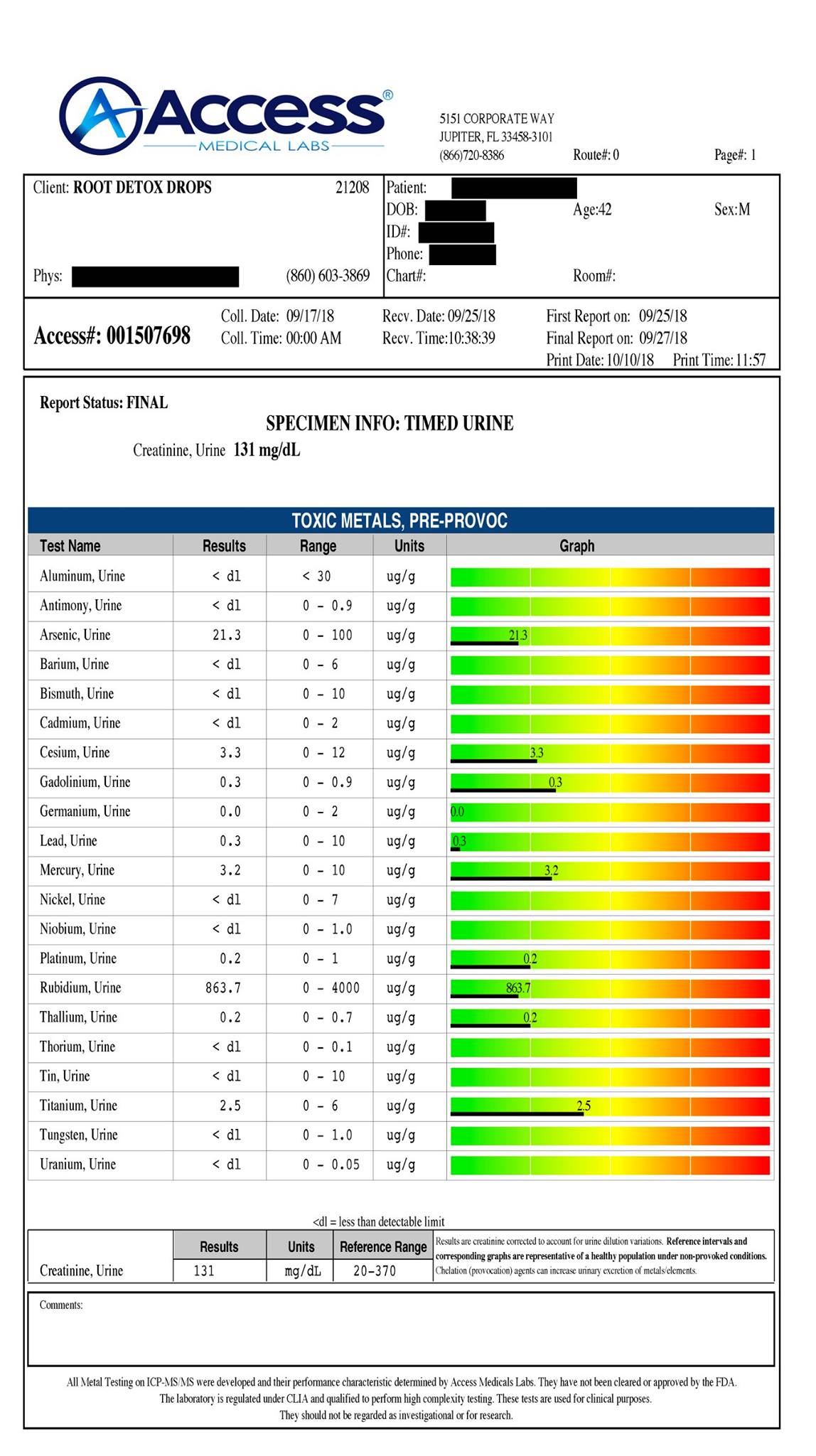
Pregnancy Complications and a Healthy Pregnancy Diet
Wrong pregnancy diet is a threat child's health. Which diet is a healthy pregnancy diet?
There are two particularly important periods in pregnancy.
The first is at the beginning when the future mother by
eating too much or too little can have an adverse influence on the
balance between the child's later food intake and growth.
The second important period is the last three or four months, when multiplication of fat cells in the child occurs.
Excessive intake of calories, carbohydrates and junk food - as is
very common in developed Western countries during pregnancy - is
considered the main reason why children are still very inclined to
obesity.
Such a pregnancy diet is associated with increased risk for diabetes and allergies in children at later age and it is definitely not a healthy pregnancy diet.
Mothers who have a body mass index above normal face the risk that their child will be born with certain diseases or physical defects and the course of their pregnancy will also be adversely affected.
Weight gain during pregnancy
According to the latest guidelines, the healthy pregnancy diet should be
such that the optimum gain weight is between 11 - 17 kg.
Excessive weight significantly increases the risks of high blood
pressure, gestational diabetes, urinary infections, phlebitis, pulmonary
embolism and gall-stones during pregnancy, and a healthy pregnancy diet
can help you avoid them.
It is not only important how much weight you gain, but also how fast. A good schedule of weight gain would be approximately as follows:
- First trimester - due to nausea and morning sickness you will probably not gain more than 1 - 2.5 kg
- Second and third trimesters - due to increased production of insulin you may constantly be hungry. Try to control the hunger by eating frequent but smaller portions so that your weight gain is about 0.5 kg per week during this period.
However, weight loss during pregnancy is not recommended!
Foods to avoid during pregnancy
- Avoid unpasteurized milk, dairy products from unpasteurized milk and
sprouts from unreliable sources. These foods can be a source of
dangerous bacteria such as Salmonella, Echerichia coli, Listeria and
Shigella.
- Avoid raw meat, fish and eggs.
- Avoid large fish such as tuna, mackerel, swordfish and shark because they may be contaminated with mercury.
- Avoid soft cheeses from unpasteurized milk - Brie, Camembert, Roquefort, Feta and Gorgonzola.
- Avoid processed meats which are not pre-cooked.
- Avoid alcohol.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy may harm your unborn child.
- Avoid herbal teas because not enough is known about their impact during pregnancy (especially avoid the herb Comfrey, which can cause severe liver disease).
...and you should also:
- Wash your hands often.
- Wash food ingredients thoroughly. Always separate raw meat from other foods.
- Food in a refrigerator must not be left at room temperature longer than two hours.
- Limit your intake of artificial sweeteners (chewing gums, soft
drinks, puddings, candy, etc.) Although there are no specific
recommendation for or against their usage, it is better to limit their
usage during pregnancy.
- Limit the intake of caffeine (coffee, black tea, cola).
- Fresh food should be the basis of your diet. Processed and canned food should be eaten only occasionally.
- Be careful not to take excessive amounts of vitamin A through
supplements. This vitamin in excessive amounts can have a teratogenic
effect.
- Take prenatal vitamins as supplements for your pregnancy diet.
- Take omega 3 fatty acids.
Vitamins and minerals

Healthy food is much more important for a healthy pregnancy diet than taking vitamins and minerals as food supplements.
However, in the diet of a pregnant woman there are four vitamins (folic
acid, B-6, D and E) and four minerals (calcium, magnesium, iron and
zinc) that are usually missing.
Iron is required for placenta and the unborn baby, and
the needs for iron are increased during pregnancy.
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy pregnancy diet because it provides necessary and healthy food ingredients (enough protein - mainly from fish, carbohydrates mainly from fruit and vegetables and the healthiest fat - olive oil).
Nutrition during pregnancy should be varied.
Having a varied diet is very important as it will help to ensure
adequate daily intake of recommended vitamins and minerals. A poor
pregnancy diet can have numerous consequences on the physical and mental
health of your child.
Drink plenty of fluids, eat more often but in smaller portions.
Breastfeeding and obesity
Obesity can also affect breastfeeding mothers.
Compared to women with a normal weight, obese mothers are significantly less likely to have enough milk for breastfeeding.
However, eating something sweet or occasionally overeating will not affect a healthy pregnancy.
Sometimes you should give yourself a break. This is probably the
happiest period of your life, and happiness of a future mother is very,
very important!
Return from Healthy Pregnancy Diet page to Home Page
SUBSCRIBE
to Mediterranean Diet Newsletter and get a FREE E-BOOK:
Printable Weekly Diet Meal Plan With Instructions!